| Family: | Fabaceae, Leguminosae |
|---|---|
| Common name: | pea family [Zomlefer, pp. 160-166] |
| Diversity: | Worldwide: 600-700 genera; ~17,000 species U.S.: ~140 genera PNW (Hitchcock & Cronquist): 23 genera |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Flower | |
|---|---|
K(5) Co5 or 1+2+(2) S9+1, 10, 10-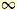 P1 P1 |
|
| Sexuality: | bisexual |
| Symmetry: | zygomorphic, some actinomorphic (Mimosoideae) |
| Inflorescence: | raceme, also umbel, heads |
| Calyx (sepals): | 5, connate |
| Corolla (petals): | 5, free or lower two fused, unequal if zygomorphic |
| Androecium: | 10 to numerous stamens; free, monadelphous, or diadelphous (9+1) |
| Gynoecium: | unicarpelate, superior ovary (=hypogynous), marginal placentation |
| Fruit: | legume (dry, dehiscent along both margins) or loment (constrictions between seeds) |
| Other features: | |
| Vegetative Features | |
|---|---|
| roots often with bacterial nodules (N2 fixation) | |
| Leaves: | alternate, compound (pinnately, less often palmately) or simple, stipulate. |
| Life-history: | annuals to perennial |
| Habit: | herbs, shrubs, trees, and vines |
| Distribution & Ecology: | cosmopolitan, Papilionoidieae is only group well represented in temperate regions of N. and S. hemispheres |
| Some Northwest Genera: | Astragalus, locoweed Lathyrus, sweet pea Lotus, deer-vetch, trefoil Lupinus, lupine Trifolium, clover Vicia, vetch |
| Economic Importance | |
|---|---|
| Crops: | Glycine, soybean Medicago, alfalfa Phaseolus, beans Pisum, peas Cicer, chick pea Lens, lentil Trifolium, clover |
| Ornamentals: | Wisteria, Lupinus, lupine |
| Weedy and pest species: | Melilotus, white sweet clover Cytisus, Scot's broom Ulex, gorse |
| Examples | Leguminosae Astragalus |
|---|---|
| Leguminosae Cytisus |
|
| Leguminosae Lotus |
|
| Leguminosae Lupinus |
|
| Leguminosae Trifollium |
|
| click on the genus name for a flower image | |
Links to Other Web Sites