Social Dominance in Spotted Hyenas
Biology 342 Fall 2015
Elaine Kushkowski & Duncan Herb
Phylogeny
Carnassial Premolars
The spotted hyena, unlike its smaller cousins, developed over the course of its evolution a set of carnassial premolars. These conically shaped teeth give the spotted hyena an incredible dietary advantage, in that rather than being forced to scavenge carcasses like its cousins, the hyena’s incredibly powerful bite, adapted to snap bones for the marrow, became an effective killing tactic, and allowed the species to become pack hunters, with the combination of their powerful bite and sharp premolars easily crushing the throats of fleeing herbivores.

Image from Tumblr.
Brain Size and Structure
While physically comparable to their cousins, several phenotypic traits distinguish the spotted hyena affecting both their social behaviors and basic behavioral patterns in regards to survival. Despite having split from their last primate ancestor upwards of 85 million years ago, the cerebral structure of the hyena bears striking resemblance to our own simian relatives. The social complexity hypothesis supposes that brain size (particularly the frontal cortex) is indicative of an animalís capacity to solve complex problems and integrate new information in solitary carnivorous mammals. However, in mammals that function within a group, the greater the size of the brain, the greater the size of a maintainable group, and the greater the complexity of the social dynamics therein.
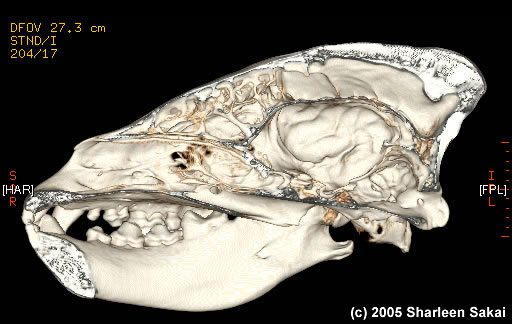
Figure 2. CT scan of adult male hyena skull. Image from Michigan State University.
Resource Distribution
Female dominance in spotted hyenas is thought to have evolved because of feeding competition and constrained skull development (Watts, 2009). Hyenas often kill prey that is much too large for one hyena to consume. Competition over the kill puts selective pressure on hyenas that can eat as much as possible in a short amount of time. Mother hyenas that can feed rapidly can provide better resources for their offspring, whose skulls are not yet developed enough to perform the bone crushing and muscle tearing motions requisite for survival. Spotted hyenas evolved into an aggressive female dominant society as a result of feeding competition and the need to provide for developing offspring.

Image from National Geographic.