The Naked Mole-Rat
Biology 342 Fall 08 -- Holly Cho and Patricia Snarski
The Naked Mole-Rat
The naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber) is, despite its name, neither naked nor a mole or a rat. It one of at least thirty different species of mole rats, which form a distinct family in the order Rodentia.
Appearance
The species is known for its unusual appearance. It is anywhere from 9-12 centimeters long, has very small eyes and ears, and large incisors that protrude in front of the mouth, as well as the nearly hairless saggy pink skin that gives rise to its name.(12)
Habitat and Behavior
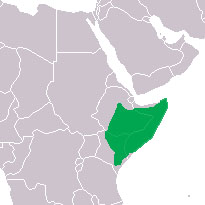
It is found in the arid climates of East Africa(12) and lives in extensive underground burrows, only occasionally emerging to search for seeds or other vegetation (11). It is an herbivore, and primarily eats roots, “farming” them by letting them regenerate after eating parts of the root, thus keeping a steady food supply in a single burrow. (12) The naked mole-rat lives in colonies of about 80 individuals, though these can grow up to colonies of 300 individuals. (12) It is known by biologists for its eusocial colony structure – it is one of only two eusocial mammals (the other being the Damaraland mole-rat).(1)
Eusociality
Eusociality is a social system found most often in insects, and it is characterized by:
- overlapping adult generations
- cooperative brood care
- more or less nonreproductive workers or helpers (1)
Eusociality is an interesting phenomenon from an evolutionary standpoint, as it is difficult to reconcile the presence of completely nonreproductive workers with traditional models of selection Darwin addressed this in The Origin of Species, admitting to difficulty in fitting eusocial colonies into his theory of selection, but proposing that workers may evolve at a colony level, despite the fact that they cannot propogate their own kind(4) One theory that has been proposed for an evolutionary mechanism for eusociality is kin selection (19) (for more information, see Adaptive Value)